Citric acid cycle 5 The biochemical process in which complex molecules are broken down into. Krebs Cycle Definition.

Different Types Of Pathways For Atp Production Microbiology Notes
Figure 2371 Digestion and Absorption.
. See answer 1 Best Answer. The small intestine is the site of most chemical digestion and almost all absorption. Chemical digestion on the other hand is a complex process that reduces food into its chemical building blocks which are then absorbed to nourish the cells of the body Figure 2371.
Not really a question. When food now churned into a substance called chyme enters the small intestine the pancreas releases its own digestive enzymes to help break down starch says Frontiers in Nutritions research. Spherical organelle that contains chromatin and nucleolus.
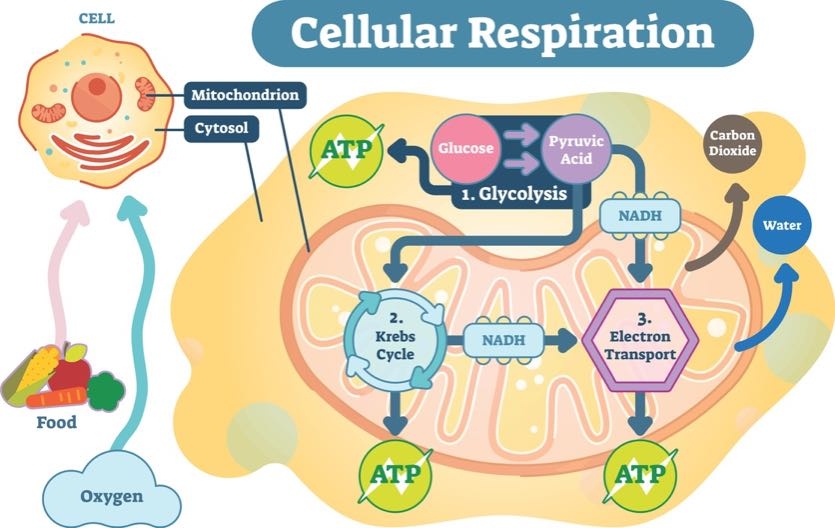
During cellular respiration the cell uses oxygen to break down sugar. Location of the energy production from digested food molecules. The energy comes from the breakdown of the whole molecule in Cell Respiration.
Food molecules are broken down in three stages to produce ATP. First oxygen needs to be presentit opens up the glucose and creates ATP which is the energy Otherwise where this occurs cellular respiration is within the cells mitochondrion-which is why it is called the. Most biochemical pathways involve coupled reactions ATP is the most common energy carrier This is why examinations of metabolic products focus on ATP production Other molecules can also act as exergonic energy carriers to help drive an endergonic biochemical reaction Examples.
NADH and FADH 2 will become familiar to you as. Most of the ATP molecules are made by the ATP synthase enzyme in the respiratory chain. Location of ATP production from digested food molecules 3.
After glycolysis breaks glucose into smaller 3-carbon molecules the Krebs cycle transfers the energy from these molecules to electron carriers which will be used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP. Location of ATP production from 3. The energy is called ATP.
C6H12O6 6O2 enzymes coenzymes 6CO2 6H2O Release of Energy 38 ATP Heat. Section 201 3 A negative DG delta G value shows a spontaneous reaction. This is an effective pathway of ATP production for short periods of time ranging from seconds to a few minutes.
The ATP synthesis occurs in the inner membrane or layer of mitochondria. In order to make ATP you need food sugar and oxygen. Since this requires oxygen it is called oxidative phosphorylation.
In this case energy is produced in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP through a process called cellular respiration a group of pathways that produces useable energy from simple food. Location of ATP production from digested food molecules Nuclear envelope Separates nuclear contents from cytoplasm Nucleous Dense body of RNA within the nucleus Nucleus Spherical organelle that contains chromatin and nucleolus Ribosome Small RNA-containing particles for the synthesis of proteins Vesicle. Stage 3 is entirely confined to the mitochondrion.
This enzyme enters the small intestine through the pancreatic duct and gets to work on deconstructing starch into smaller chains and individual molecules. Loosely coiled fiber containing DNA and protein within nucleus 2. Vesicle Column B 1.
Stage 2 starts in the cytosol and ends in the major energy-converting organelle the mitochondrion. The Krebs Cycle also called the citric acid cycle is the second major step in oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondria is the organelle where the oxidative phosphorylation process takes place in many plant and animal cells.
Powerhouse of cell Location of ATP production from digested food molecules. 10 protons pumped by NADH. Your body cells use the oxygen you breathe to get energy from the food you eat.
The Generation of Biochemical Energy 1 What are the end products in the oxidation of food molecules CHO containing compounds. Dense body of RNA within nucleus 6. Where are mitochondria located.
If you dont have food you cant make ATP and youre going to die. Even if I brought in all the food in the world and. As illustrated in Figure 2-70 oxidation occurs in two further stages of cellular catabolism.
Separates nuclear contents from cytoplasm. Membranous sac that stores or transports substances 5. E digestion.
Dense body of RNA within the nucleus. The lactic acid produced diffuses into the plasma and is carried to the liver where it is converted back into pyruvate or glucose via the Cori cycle. This process is called cellular respiration.
C H O food moleculesO2 CO2H20 energy 2 List some of the specific requirments we have for energy. Here is the overall simplified reaction for aerobic respiration. Mitochondria are structures within cells that convert the energy from food into a form that cells can use.
Small RNA-containing particle for synthesis of proteins 4. In this section you will look more closely at the processes of chemical digestion and absorption. Chemical digestion breaks large food molecules down into their chemical building blocks which can then be absorbed through the intestinal wall and into the general circulation.
Scientists dont yet know exactly how many protons are pumped in the respiratory chain but the current estimates are. After digestion the small organic molecules derived from food enter the cytosol of the cell where their gradual oxidation begins. First the enzymatic breakdown of food molecules during digestion.
And 4 protons needed by ATP synthase to make one ATP. Cell Structure and Function a Chromatin b Cytoplasm c Endoplasmic reticulum d Golgi apparatus e Lysosome f Microtubule g Mitochondrion h Nuclear envelope protein and DNA within nucleus digested food molecules the synthesis of proteins pinching off of pieces of cell membrane 1.

Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists
How Does The Energy In Food Get Transferred To Molecules In Cells That Do Work Like Make A Muscle Cell Contract Or Build A Protein Quora

0 Comments